This comprehensive guide provides detailed answers to all questions from the November/December 2022 Level Two Computer Systems for Business examination. Use this interactive resource to enhance your understanding and prepare effectively for your exams.
Click above to download the complete question paper for offline study
SECTION A (50 MARKS)
1. a. What is a notebook computer?
A notebook computer (commonly called a laptop) is a portable personal computer designed for mobile use that integrates all typical components of a desktop computer into a single unit. It features:
- A thin LCD or LED computer screen
- An alphanumeric keyboard
- A pointing device (touchpad or trackpoint)
- Rechargeable battery power
- Significantly reduced size and weight compared to desktops
Notebook computers are designed to be easily carried and used in temporary spaces like libraries, meetings, airplanes, etc. They typically weigh between 1-3 kg and can perform most tasks that desktop computers can perform.
b. State TWO (2) examples of notebook computer brands.
Popular notebook computer brands include:
- Dell (e.g., Dell XPS, Dell Inspiron)
- HP (Hewlett-Packard) (e.g., HP Spectre, HP Envy)
- Lenovo (e.g., Lenovo ThinkPad, Lenovo Yoga)
- Apple (MacBook Pro, MacBook Air)
- Acer (e.g., Acer Aspire, Acer Swift)
- ASUS (e.g., ASUS ZenBook, ASUS VivoBook)
2. Outline FIVE (5) preventive maintenance procedures that can be carried out to ensure safety of a computer in terms of software and hardware.
Software Maintenance:
- Regular Updates: Keep operating system and applications updated with latest security patches and bug fixes to protect against vulnerabilities.
- Antivirus Protection: Install and regularly update antivirus software to detect and remove malware, with scheduled full system scans.
- Data Backup: Implement regular backup procedures (daily/weekly) to external drives or cloud storage to prevent data loss.
Hardware Maintenance:
- Proper Ventilation: Ensure adequate airflow around computer components to prevent overheating, with regular cleaning of fans and vents.
- Power Protection: Use surge protectors or UPS systems to safeguard against power fluctuations and outages.
- Cable Management: Organize cables to prevent tripping hazards and reduce strain on ports and connectors.
- Regular Cleaning: Clean keyboards, screens, and other components with appropriate materials to prevent dust buildup.
3. Take Engineering Ltd intends to embrace ergonomic standards in all its computer facilities. State FIVE (5) benefits that the company could realize from this decision.
Implementing ergonomic standards in computer facilities provides several benefits:
- Reduced Health Issues: Minimizes musculoskeletal disorders (like carpal tunnel syndrome) and eye strain among employees.
- Increased Productivity: Comfortable employees can work longer with less fatigue, maintaining higher productivity levels.
- Lower Absenteeism: Fewer work-related injuries lead to reduced sick days and lower healthcare costs.
- Improved Employee Morale: Shows concern for employee wellbeing, increasing job satisfaction and retention.
- Legal Compliance: Meets occupational health and safety regulations, reducing liability risks.
- Better Work Quality: Comfortable employees make fewer errors and produce higher quality work.
- Cost Savings: Reduces long-term costs associated with workplace injuries and employee turnover.
4. a. Distinguish between stress and fatigue with regards to using a computer.
| Stress | Fatigue | |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Psychological response to perceived pressure or demands when using computers | Physical or mental exhaustion from prolonged computer use |
| Primary Cause | Workload, time pressure, technical difficulties, information overload | Prolonged static posture, repetitive movements, eye strain |
| Manifestations | Anxiety, irritability, difficulty concentrating, feeling overwhelmed | Muscle soreness, headaches, drowsiness, decreased alertness |
| Timeframe | Can occur quickly in response to immediate pressures | Develops gradually over extended periods of use |
| Affected Areas | Primarily mental/emotional state | Both physical body and mental capacity |
b. State ONE (1) preventive way to avoid stress or fatigue when using a computer.
Effective preventive measures include:
- Take Regular Breaks: Follow the 20-20-20 rule (every 20 minutes, look at something 20 feet away for 20 seconds) and take 5-10 minute breaks every hour.
- Ergonomic Setup: Adjust chair height so feet rest flat, position monitor at eye level, keep wrists straight while typing.
- Proper Lighting: Ensure adequate ambient lighting to reduce eye strain, avoid glare on screen.
- Task Variation: Alternate between different types of tasks to avoid prolonged repetitive motions.
- Stress Management: Practice relaxation techniques like deep breathing when feeling stressed.
5. With the aid of diagrams in each case, explain TWO (2) categories of computer networks based on how information is shared.
1. Client-Server Network:
In this architecture, one or more powerful computers (servers) provide services to multiple client computers. The server manages network resources and fulfills requests from clients.

- Centralized control: All data stored on servers
- Scalable: Easy to add more clients
- Secure: Centralized security management
- Examples: Corporate networks, web applications
2. Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Network:
In this decentralized model, all computers (peers) have equal status and can act as both clients and servers, sharing resources directly without a central server.
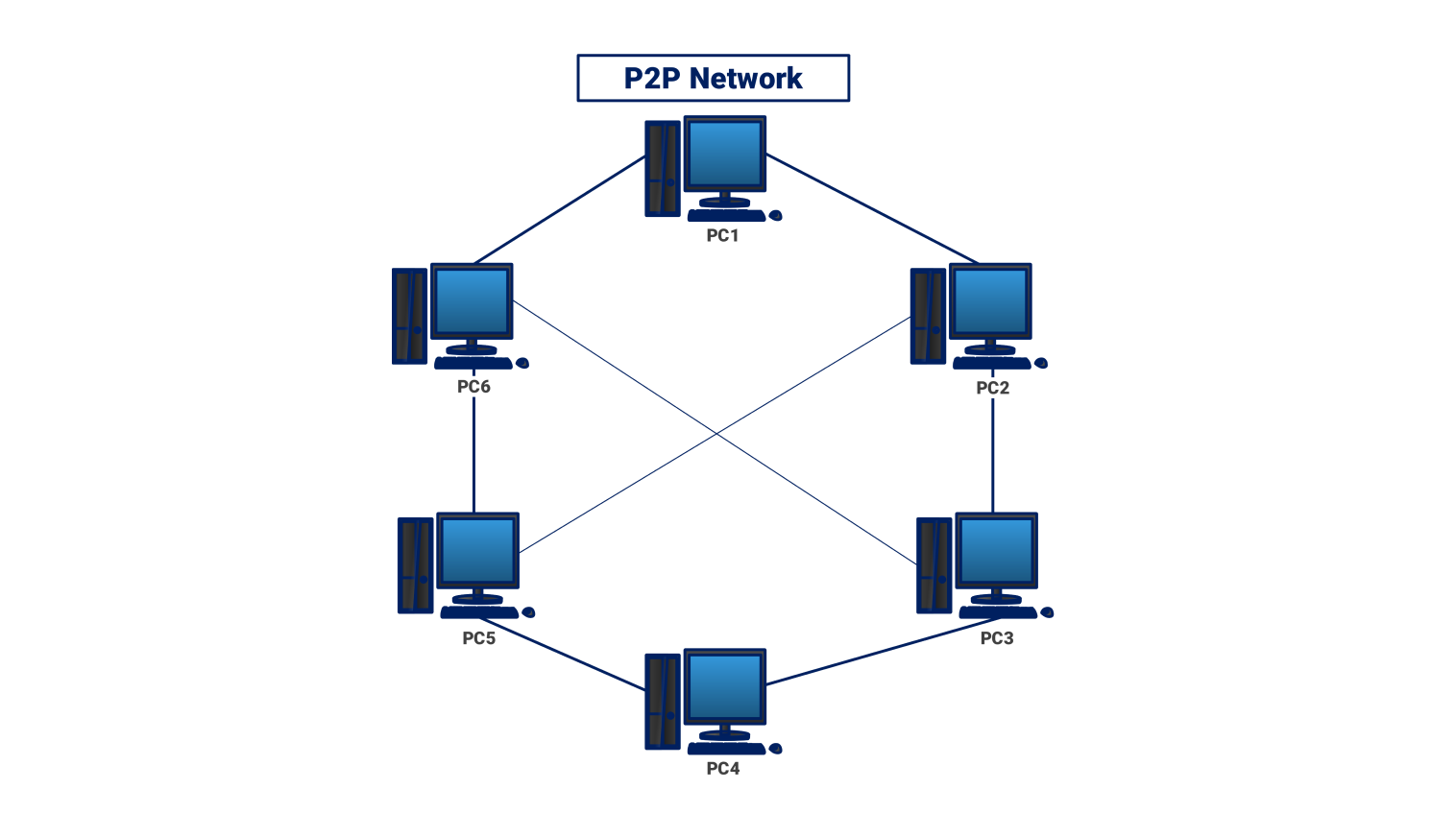
- Decentralized: No central authority
- Resource sharing: Each peer can share files/resources
- Less expensive: No need for dedicated servers
- Examples: File sharing networks, blockchain systems
6. a. What is a supercomputer?
A supercomputer is the fastest and most powerful type of computer, used for complex scientific calculations, weather forecasting, and simulations.
b. State TWO (2) advantages of a laptop computer over a desktop computer.
- Portability Laptops are easy to carry and use anywhere.
- Built-in battery Laptops can be used even during power outages.
7. a. Define ICT Ethics.
ICT Ethics are rules and principles that guide proper use of computers, internet, and information technology to ensure honesty, privacy, and respect.
b. Explain TWO (2) advantages of embracing ICT ethics in an organization.
- Promotes trust and integrity among employees and clients.
- Reduces cybercrime and misuse of technology resources.
8. a. Distinguish between ROM and RAM used in computers.
- ROM (Read Only Memory) Stores permanent data that is not erased when the computer is turned off.
- RAM (Random Access Memory) Stores temporary data for running programs, and is cleared when the computer shuts down.
b. Which of the above memories can be replaced easily by a user when damaged?
RAM can be replaced easily by a user.
9. a. Differentiate between mainframe and mini computers
- Mainframe computers Large, powerful systems used by big organizations for processing massive data.
- Mini computers Smaller and less powerful than mainframes, used by small to medium sized businesses.
b. Which of the above computers is cheaper to purchase?
Mini computers are cheaper to purchase.
10. Magnetic disk is a popular computer storage medium. Outline FIVE (5) advantages of this storage medium.
- Reusable Data can be erased and rewritten.
- Large storage capacity
- Relatively low cost
- Fast access to data
- Portable and easy to handle
SECTION B (50 MARKS)
1. a. Define BIOS.
BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) is firmware used to perform hardware initialization during the booting process (power-on startup) and to provide runtime services for operating systems and programs. It is the first software that runs when a computer is powered on, stored on a chip on the computer's motherboard.
Key characteristics of BIOS:
- Non-volatile firmware (retains settings when power is off)
- Stored on a ROM chip (modern systems use flash memory)
- Provides lowest-level interface between hardware and OS
- Performs Power-On Self-Test (POST) to check hardware
- Contains configuration settings accessible via BIOS setup utility
b. State TWO (2) functions of BIOS.
Primary functions of BIOS include:
- POST (Power-On Self-Test): Checks computer hardware before loading the OS to ensure all components are functioning properly.
- Bootstrap Loader: Locates and loads the operating system into memory from storage devices.
- Hardware Configuration: Identifies, configures, and initializes system hardware components.
- CMOS Setup: Provides interface for system configuration (date/time, boot order, hardware settings).
- Basic Hardware Control: Provides basic input/output operations for keyboard, display, storage, etc.
2. a. Differentiate between memory and storage
| Memory (RAM) | Storage | |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Temporary workspace for active programs and data | Permanent retention of programs and data |
| Volatility | Volatile (loses data when power is off) | Non-volatile (retains data without power) |
| Speed | Very fast (nanosecond access) | Slower (millisecond access) |
| Capacity | Typically 4GB-128GB in modern systems | Typically 256GB-4TB in modern systems |
| Physical Form | Memory modules (DIMMs) on motherboard | Hard drives, SSDs, flash drives, optical media |
| Cost | More expensive per GB | Less expensive per GB |
b. State ONE (1) example each.
Memory Examples:
- DRAM (Dynamic RAM)
- SDRAM (Synchronous DRAM)
- DDR4/DDR5 RAM
Storage Examples:
- Hard Disk Drive (HDD)
- Solid State Drive (SSD)
- USB Flash Drive
- CD/DVD/Blu-ray
3. Explain computer virus. Give TWO (2) examples.
A computer virus is a type of malicious software program designed to harm, disrupt, or gain unauthorized access to computer systems.
-
Examples:
- Trojan Horse
- WannaCry Ransomware
4. a. What is Phishing?
Phishing is a cybercrime where attackers pretend to be trustworthy sources (like banks or websites) to trick people into giving sensitive information like passwords or credit card numbers.
b. State TWO (2) means of ensuring computer security
- Installing and updating antivirus software
- Using strong passwords and changing them regularly
5. State FIVE (5) categories of computer keyboard
- Standard keyboard
- Gaming keyboard
- Flexible keyboard
- Virtual keyboard
- Ergonomic keyboard
6. a. Differentiate between an LCD and CRT monitor.
- LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) Thin, flat, lightweight, and uses less power.
- CRT (Cathode Ray Tube) Bulky, heavy, and consumes more power.
b. What is the maximum screen size of a laptop?
Generally, 17 to 18 inches.
7. State FIVE (5) ways of protecting your privacy while using the web and internet.
- Use strong and unique passwords
- Enable two-factor authentication
- Avoid public Wi-Fi for sensitive activities
- Keep browsers and software updated
- Don’t share personal information on untrusted websites
8. a. What is an output device?
An output device is hardware that receives and displays or delivers the result of processed data from a computer.
b. Name TWO (2) examples of output device
- Monitor
- Printer
9. An NGO in the Oti region of Ghana intends to procure an operating system for office use. State FIVE (5) factors the organization should consider when procuring the software.
- Compatibility with existing hardware
- User-friendliness
- Security features
- Cost of the OS and licensing
- Technical support and updates availability
10. List FIVE (5) modern system software manufactured by Microsoft
- Windows 10
- Windows 11
- Windows Server 2019
- Microsoft Defender Antivirus
- Windows PowerShell
Exam Success Tip: Practice these questions under timed conditions to simulate the exam environment. Focus on understanding concepts rather than memorization for better application in different question scenarios.
Get the complete question paper with all sections for offline practice











